Difference between revisions of "Taglisty"
From MorphOS Library
(Created, copied English text over.) |
(Translation in progress.) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| − | + | Taglista to tablica par "klucz-wartość". Kluczem jest zawsze 32-bitowa liczba całkowita i nazywana jest ''tagiem''. Wartość ma również rozmiar 32 bitów. Może to być liczba całkowita, lub wskaźnik na dowolną strukturę, czy obiekt. Taglisty są powszechnie używane w API MorphOS-a do przekazywania zmiennej liczby argumentów, zazwyczaj listy atrybutów wraz z ich wartościami. Kilka specjalnych wartości kluczy jest używanych do zakończenia taglisty, przeskakiwania elementów i łączenia taglist. Biblioteka ''utility.library'' zawiera zestaw funkcji do przeglądania, filtrowania, przeszukiwania, kopiowania i innych operacji na taglistach. | |
| − | + | Każdy element taglisty (para klucz-wartość) jest strukturą ''TagItem'', zdefiniowaną w pliku nagłówkowym ''<utility/tagitem.h>'': | |
struct TagItem | struct TagItem | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
}; | }; | ||
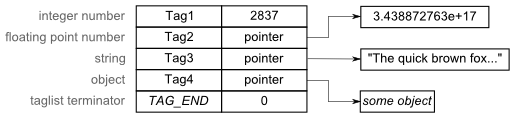
| − | + | Taglista jest zwykłą tablicą języka C, żeby była samoopisująca się, musi posiadać jakiś sposób terminacji (oznaczenia końca). Idea jest zbliżona do terminacji łańcuchów tekstowych bajtem 0. Struktura ''TagItem'' oznaczająca koniec taglisty ma pole ''ti_Tag'' ustawione na stałą ''TAG_END'' i tak się składa, że ta stała jest równa 0. Pole ''ti_Data'' kończącego elementu jest ignorowane i zwykle również bywa ustawiane na 0. Poniższa ilustracja przedstawia prostą taglistę: | |
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| − | + | Taglistę tę można zbudować następującym kodem: | |
double x = 3.438872763e+17; | double x = 3.438872763e+17; | ||
Object *obj = NewObject( /* ... */ ); | Object *obj = NewObject( /* ... */ ); | ||
| − | struct TagItem | + | struct TagItem taglista[] = { |
{ Tag1, 2837 }, | { Tag1, 2837 }, | ||
{ Tag2, (ULONG)&x }, | { Tag2, (ULONG)&x }, | ||
| − | { Tag3, (ULONG)" | + | { Tag3, (ULONG)"Leż, dość próźnych kłamstw, rąb fuzję, giń!" }, |
{ Tag4, (ULONG)obj }, | { Tag4, (ULONG)obj }, | ||
{ TAG_END, 0 } | { TAG_END, 0 } | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Taglisty jako argumenty funkcji== |
Building taglists as global or local variables is not very convenient. That is why almost every MorphOS API function getting a taglist as one of its arguments has two forms. The first one accepts a pointer to the taglist. The second one is a variadic args macro building the taglist on the program stack dynamically. Such function pairs are named according to one of the two conventions: | Building taglists as global or local variables is not very convenient. That is why almost every MorphOS API function getting a taglist as one of its arguments has two forms. The first one accepts a pointer to the taglist. The second one is a variadic args macro building the taglist on the program stack dynamically. Such function pairs are named according to one of the two conventions: | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 7 April 2011
Grzegorz Kraszewski
Taglista to tablica par "klucz-wartość". Kluczem jest zawsze 32-bitowa liczba całkowita i nazywana jest tagiem. Wartość ma również rozmiar 32 bitów. Może to być liczba całkowita, lub wskaźnik na dowolną strukturę, czy obiekt. Taglisty są powszechnie używane w API MorphOS-a do przekazywania zmiennej liczby argumentów, zazwyczaj listy atrybutów wraz z ich wartościami. Kilka specjalnych wartości kluczy jest używanych do zakończenia taglisty, przeskakiwania elementów i łączenia taglist. Biblioteka utility.library zawiera zestaw funkcji do przeglądania, filtrowania, przeszukiwania, kopiowania i innych operacji na taglistach.
Każdy element taglisty (para klucz-wartość) jest strukturą TagItem, zdefiniowaną w pliku nagłówkowym <utility/tagitem.h>:
struct TagItem
{
ULONG ti_Tag;
ULONG ti_Data;
};
Taglista jest zwykłą tablicą języka C, żeby była samoopisująca się, musi posiadać jakiś sposób terminacji (oznaczenia końca). Idea jest zbliżona do terminacji łańcuchów tekstowych bajtem 0. Struktura TagItem oznaczająca koniec taglisty ma pole ti_Tag ustawione na stałą TAG_END i tak się składa, że ta stała jest równa 0. Pole ti_Data kończącego elementu jest ignorowane i zwykle również bywa ustawiane na 0. Poniższa ilustracja przedstawia prostą taglistę:
Taglistę tę można zbudować następującym kodem:
double x = 3.438872763e+17;
Object *obj = NewObject( /* ... */ );
struct TagItem taglista[] = {
{ Tag1, 2837 },
{ Tag2, (ULONG)&x },
{ Tag3, (ULONG)"Leż, dość próźnych kłamstw, rąb fuzję, giń!" },
{ Tag4, (ULONG)obj },
{ TAG_END, 0 }
};
Taglisty jako argumenty funkcji
Building taglists as global or local variables is not very convenient. That is why almost every MorphOS API function getting a taglist as one of its arguments has two forms. The first one accepts a pointer to the taglist. The second one is a variadic args macro building the taglist on the program stack dynamically. Such function pairs are named according to one of the two conventions:
- SomeFunctionA() takes a pointer to a taglist, SomeFunction() builds the taglist dynamically.
- SomeFunctionTagList() takes a pointer to a taglist, SomeFunctionTags() builds the taglist dynamically.
Continuing the above example, one can pass the example taglist to SomeFunction() in two ways:
SomeFunctionTagList(mytaglist); SomeFunctionTags(Tag1, 2837, Tag2, (ULONG)&x, Tag3, (ULONG)"The quick brown fox...", Tag4, (ULONG)obj, TAG_END);
Of course in the second case variable mytaglist need not be defined anywhere. Note that for every taglist-based function the taglist is the last argument. There may be some plain arguments before it. It is a common practice to omit ti_Data for the terminator (it is ignored anyway).