Difference between revisions of "Subclassing Application Class"
From MorphOS Library
m (→Creating Buttons: Style.) |
m (→Creating Buttons: Style.) |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
====Creating Buttons==== | ====Creating Buttons==== | ||
| − | As said above, a text button is an instance of the ''Text'' class too. It has more attributes than a plain label however. ''MUIA_Text_PreParse'' attribute centers the text in the object. | + | As said above, a text button is an instance of the ''Text'' class too. It has more attributes than a plain label however. ''MUIA_Text_PreParse'' attribute centers the text in the object. After setting a frame and a background, a proper font is also specified with ''MUIA_Font''. Forgetting this attribute is one of common interface design errors. Next four attributes are related to user input. ''MUIA_InputMode'' attribute defines type of button (push or toggle one). ''MUIA_CycleChain'' makes the button reachable with keyboard. Incomplete keyboard support for GUI is another common error. All gadgets receiving user input should have ''MUIA_CycleChain'' set. Most important gadgets should be also reachable with single keys. ''MUIA_ControlChar'' sets a key, which activates the gadget. For textual gadgets a letter of this key should be also underlined with ''MUIA_Text_HiChar''. It implies that the character used should be present in the gadget label. Both these attributes should be set to small letters. ''MUIA_ControlChar'' set to a capital letter will force user to press ''SHIFT''. ''MUIA_Text_HiChar'' is case insensitive. Digits can be also used for control characters, if button labels contain them. Using other characters is strongly discouraged. |
Object* create_button(char *label, char control) | Object* create_button(char *label, char control) | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 2 January 2011
Grzegorz Kraszewski
Contents
Introduction
Every MUI application is (or at least should be) an event driven one. It means the application provides a set of actions, which may be triggered with user activity (like using mouse and keyboard). The straightforward way of implementing this set of actions is to implement it as a set of metods added to some MUI object. For simple programs, the best candidate for adding such methods is the master Application object. More complex programs (for example ones using multi-document interface) may add actions to other classes, for example Window one.
Why methods? Implementing actions as methods has many advantages:
- Methods may be used directly as notification actions. It saves a programmer from using hook tricks or cluttering the main loop with teens of ReturnID values.
- Methods may be coupled directly with scripting language interface (formerly known as ARexx interface) commands.
- Methods used in notifications are executed immediately in response of user actions. No delay is introduced by the main loop (especially if it is not empty).
- A notification triggering attribute value may be passed directly to method, as its parameter.
- Using methods improves code modularity.
The Application
Many programming tutorials tend to bore readers with some useless examples. In this one a "real world" application will be ported to MorphOS and "MUI-fied". The application is SciMark 2. SciMark is yet another CPU/memory benchmark. It performs some typical scientific calculations like Fast Fourier Transform, matrix LU decomposition, sparse matrix multiplication and so on. The benchmark measures mainly CPU speed at floating point calculations, cache efficiency and memory speed. Being written in Java initially, it has been rewritten in C (and in fact in many other languages). The C source is available on the project homepage.
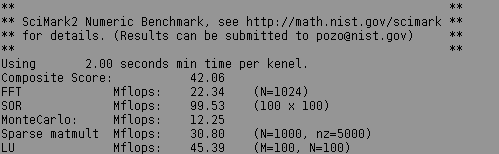
The source uses only pure ANSI C standard, so it is easily compilable on MorphOS using provided Makefile. One has just replace $CC = cc line to $CC = gcc, to match the name of the MorphOS compiler. As a result, a typical shell-based application is obtained. Here are example results for a Pegasos 2 machine with G4 processor:
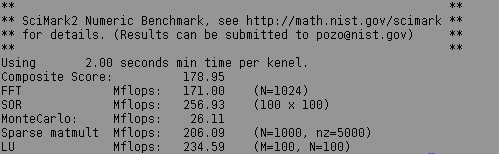
Not very impressive in fact. This is because no optimizaton flags are passed to the compiler in the makefile. They can be added by inserting a line $CFLAGS = -O3 below the $CC = gcc one. Let's also link with libnix (a statically linked unix environment emulation, see Standard C and C++ Libraries) by adding -noixemul to CFLAGS and LDFLAGS. After rebuilding the program and running it again the results are significantly improved (the program has been compiled with GCC 4.4.4 from the official SDK).
This shows how important is optimization of the code, especially computationally intensive one. Optimized code is more than 4 times faster!
Code Inspection
The original source code is well modularized. Five files: FFT.c, LU.c, MonteCarlo.c, SOR.c and SparseCompRow.c implement the five of single benchmarks. Files array.c and Random.c contain auxiliary functions used in benchmarks. File Stopwatch.c implements time measurement. An important file kernel.c gathers all the above and provides five functions performing complete benchmarks with timing. Finally scimark2.c contains the main() function and implements the shell interface.
A planned MUI interface should allow to run every benchmark separately and run all of them. There is also -large option, which increases memory sizes of calculated problems, so they do not fit into the processor cache. A general rule of porting is that as few files as possible should be modified. The rule makes it easier to upgrade the port when a new version of original program is released. In the case of SciMark, only one file, scimark2.c has to be replaced. An advanced port may also replace Stopwatch.c with code using timer.device directly for improved time measurements accuracy, this is out of scope of this tutorial however.
GUI Design
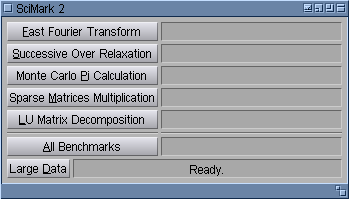
Of course there is no one and only proper GUI design for SciMark. A simple design, using a limited set of MUI classes is shown on the left. There are five buttons for individual benchmarks and one for running all of them. All these buttons are instances of the Text class. On the right there are gadgets for displaying benchmark results. These gadgets belong to Text class too, just having different attributes. The "Large Data" button, of Text class of course, is a toggle one. Surprisingly the status bar (displaying "Ready.") is not an instance of the Text class, but Gauge class. Then it will be able to display a progress bar when running all five tests. Spacing horizontal bars above the "All Benchmarks" button are instances of the Rectangle class. There are also three invisible objects of the Group class. The first is a vertical, main group, being the root object of the window. It contains two sub-groups. The upper one is the table group with two columns and contains all the benchmark buttons and result display gadgets. The lower group contains "Large Data" toggle button and the status bar.The simplest way to start with GUI design is just to copy the "Hello World" example. Then MUI objects may be added to build_gui() function. The modified example is ready to compile and run. It is not a complete program of course, just a GUI model without any functionality added.
A quick view into the build_gui() function reveals that it does not contain all the GUI code. Code for some subobjects is placed in functions called from the main MUI_NewObject(). Splitting the GUI building function into many subfunctions has a few important advantages:
- Improved code readability and easier modifications. A single MUI_NewObject() call gets longer and longer quickly as the project evolves. Editing a large function spanning over a few screens is uncomfortable. Adding and removing GUI objects in such a function becomes nightmare even with indentation used consequently. On the other hand the function can have 10 or more indentation levels, which makes it hard to read as well.
- Code size reduction. Instead of writing very similar code multiple times, for example buttons with different labels, a subroutine may be called with label as an argument.
- Debugging. It happens sometimes that MUI refuses to create the application object because of some buggy tags or values passed. If the main MUI_NewObject() call is splitted into subfunctions, it is easy to isolate the buggy object by inserting some Printf()-s in subfunctions.
Creating Textfields
The Text MUI class is used not only for creating static texts or labels (like in the "Hello World!" example), but also framed readonly text gadgets and textual buttons. All these object differ only in attributes. A read-only framed text field has a specific background and frame:
Object* create_resdisplay(void)
{
Object *obj;
obj = MUI_NewObject(MUIC_Text,
MUIA_Frame, MUIV_Frame_Text,
MUIA_Background, MUII_TextBack,
TAG_END);
return obj;
}
Creating Buttons
As said above, a text button is an instance of the Text class too. It has more attributes than a plain label however. MUIA_Text_PreParse attribute centers the text in the object. After setting a frame and a background, a proper font is also specified with MUIA_Font. Forgetting this attribute is one of common interface design errors. Next four attributes are related to user input. MUIA_InputMode attribute defines type of button (push or toggle one). MUIA_CycleChain makes the button reachable with keyboard. Incomplete keyboard support for GUI is another common error. All gadgets receiving user input should have MUIA_CycleChain set. Most important gadgets should be also reachable with single keys. MUIA_ControlChar sets a key, which activates the gadget. For textual gadgets a letter of this key should be also underlined with MUIA_Text_HiChar. It implies that the character used should be present in the gadget label. Both these attributes should be set to small letters. MUIA_ControlChar set to a capital letter will force user to press SHIFT. MUIA_Text_HiChar is case insensitive. Digits can be also used for control characters, if button labels contain them. Using other characters is strongly discouraged.
Object* create_button(char *label, char control)
{
Object *obj;
obj = MUI_NewObject(MUIC_Text,
MUIA_Text_Contents, (ULONG)label,
MUIA_Text_PreParse, "\33c",
MUIA_Frame, MUIV_Frame_Button,
MUIA_Background, MUII_ButtonBack,
MUIA_Font, MUIV_Font_Button,
MUIA_InputMode, MUIV_InputMode_RelVerify,
MUIA_Text_HiChar, control,
MUIA_ControlChar, control,
MUIA_CycleChain, TRUE,
MUIA_HorizWeight, 1,
TAG_END);
return obj;
}
Creating Spacing Bars
Object* create_hbar(void)
{
Object *obj;
obj = MUI_NewObject(MUIC_Rectangle,
MUIA_Rectangle_HBar, TRUE,
MUIA_FixHeight, 2,
TAG_END);
return obj;
}
Creating Gauge
Object* create_statusbar(void)
{
Object *obj;
obj = MUI_NewObject(MUIC_Gauge,
MUIA_Frame, MUIV_Frame_Gauge,
MUIA_Font, MUIV_Font_Gauge,
MUIA_Background, MUII_TextBack,
MUIA_Gauge_Horiz, TRUE,
MUIA_Gauge_InfoText, (ULONG)"Ready.",
TAG_END);
return obj;
}